 Five RRLs (Regional Research Laboratories) has been renamed by the CSIR (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research) to enable them to present an outlook that is futuristic.
According to the CSIR spokesman, the profiles of the laboratories, which were changed with respect to their orientation of expertise, direction of growth, and excellence accumulated have all been evaluated while renaming them. The changing of name took effect starting 6 March this year.
RRL-Bhubaneswar has been renamed as IMMT (Institute of Minerals and Materials Technology); RRL-Bhopal was renamed as AMPRI (Advanced Materials and Processes Research Institute); and RRL-Jammu as IIIM (Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine).
RRL-Thiruvananthapuram, was also renamed and it is now NIIST (National Institute for Interdisciplinary Science and Technology) and RRL-Jorhat will be known now as NEIST (North - East Institute of Science and Technology).
Having 47 regional centres and 38 laboratories, the CSIR is a leading autonomous R&D organisation. It takes on research and development activities that cover the entire picture in the civilian sector of science and technology.
Through the Central Legislative Assembly resolution that was constituted in 1942, it intends to provide social welfare, advancement of fundamental knowledge, industrial competitiveness, strong science and technology base for strategic sectors.
The multi-disciplinary research and development laboratory, RRL-T at the Industrial Estate at Pappanamcode is keenly engaged in applied and basic research as it seeks to fill the needs of the region in agro energy, products and materials, which explains its new nomenclature.
 The police and insurance companies only need a careless touch to determine not just the person’s identity, but also their criminal history and definite medical conditions.
Professor David Russell at the University of East Anglia said: "A fingerprint is only good to identify a criminal if you already have their fingerprint on file". Along with Dr. Pompi Hazarika, the two helped each other to develop a new technique that will appear in the German journal. Russell said: "This will give police new tools to help discover that identity".
For decades, scientists have dusted fingerprints using magnetic particles to expose the hidden curls and swirls that distinguish every person on the world. Iron oxide particles connect to the tiny bits of oil, mineral and water that will accumulate on someone’s fingers as they touch any object. The new technique and this iron oxide particles combine with antibodies and suspend both in a liquid solution that is then moistened over a fingerprint. To this point, the scientists can only detect five different drugs, which include methadone, a derivative of methadone, nicotine, cocaine and THC (marijuana). Other drugs, mostly opium-based drugs such as morphine and heroine, should also be noticeable or detectable, since antibodies exist for them to use.
In medical history, drugs are not the only chemical that the new test can detect. Heart failure, cancer, diabetes and other medical conditions can also be detected.
 According to an expert in speech analysis, popular crime shows in TV might be interesting to public, but the shows may be delivering an unrealistic notion of the significance of science in this field.
"Most dramas include this kind of thing [and] there's a great deal of poetic licence in what they do", says Dr. Paul Foulkes, phonetics and linguistics expert of York University.
Foulkes is providing training in the field of forensic speech analysis for the FBI and the United States Secret Service.
According to his speech at the meeting of ARC Network in Human Communication Science, The Forensic Speech Science involves phonetic, acoustic and linguistic examination of recordings that can be useful to try and pin down possible suspects. Moreover, it is also useful to verify how well a voice of the suspect matches a voice of the criminal.
Foulkes says that speech recording cannot be used to identify the voice of someone with sureness on its own.
"There is no such thing as a voice print", Foulkes says. "It's a very dangerous term. There is no single feature of a voice that is indelible that works like a fingerprint does".
According to him, there are several factors that influence how people talk.
Though speech analysis cannot be applied to identify the voice of someone with certainty, it can be used to trim down the number of suspected persons.
 For the past decades, first world and third world countries are starting to close the gap brought about by space aspirations and achievements.
For over 50 years, the United States have dominated space science and exploration, spearheading moon landings, space flights, travel to far planets, launch of almost 4,000 surveillance and communication satellites, and development of multination space station.
Developing nations such as China has also embarked on extensive space programmes, developed satellite vehicles and launch sites, and carried out manned space flights. In addition, China has announced its plan to launch an unmanned robotic mission to the moon, aiming to explore lunar mining, and establish a space station, probably in collaboration with other third-world countries. Other plans consist of astrophysics research, which include a deep-space tracking network that involves the world’s biggest radio antennae and the launch of the world’s biggest solar space telescope.
Pakistan, Nigeria, Malaysia, Iran, Indonesia, Egypt, Argentina and Algeria have already owned and operated satellites, which they utilised to enhance communications, national defence, environmental protection and agriculture. Brazil and India also have capabilities for a satellite launch.
Space programmes critics have argued that it is better for developing countries to spend funding on healthcare and the construction of universities and infrastructure rather than in space industry, failing to acknowledge that the science and technology of space can have vital contributions to the most critical economic and social needs of a country and can also transform industrialization.
 Members of Parliament have notified that the scientific research in the seas is unsystematic and underfunded in spite of its significance to human living.
According to the members of Science and Technology Select Committee, United Kingdom has the capability to be on the lead in marine science. For them, the UK is a field of research, which could contribute to almost every industry sector, from healthcare to cosmetics.
On the other hand, a report made by the Members of Parliament stated that funding over the previous decade has descended in actual terms. The sector of marine science and technology received only £5.4 million fund in 2006, which is remarkably less compared to the fund given in 2003 and 2004.
The Members of Parliament said that the oceans should be “explored, monitored, studied and understood more thoroughly than has been the case up to now”. They are extremely disappointed because they all know that the marine sector is very important with regards to climate, food supply, biodiversity, and renewable energy resources.
As a result, the committee demanded to set up a new marine agency in order to manage ocean monitoring and marine science. In addition, it will also promote the education in schools and to the public.
Aside from that, the Members of Parliament also advised the government to move forward a summary of Marine Bill without any delay.
 Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute in Florida Atlantic University (Harbor Branch) was chosen by Waitt Institute for Discovery to accomplish series of travel exploration in Straits of Florida. The Waitt, with Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, is building unmanned, available cutting edge, deep ocean expedition device called autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs).
The exploration used the AUV’s in creating quality sonar maps of the deep-water Lophelia coral reefs. The Deep Sea Coral Ecosystems (DSCEs) are now under threat from the devastating bottom trawling and human-caused impacts.
The exploration is headed by research professor John Reed, who was working and studying in protecting deep corals for more than 30 years.
For the first exploration, Harbor Branch contributes ocean expedition expertise, exploration logistics, science plan execution and development and expedition resources that include research craft Seward Johnson.
CATALYST is a partnership between Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Waitt Institute for Discovery in completing series of deep sea explorations.
As founder of CATALYST Program, Waitt Institute for Discovery accredited the building of two REMUS 6000 AUVs and presently directs implementation of the CATALYST explorations.
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution built and designed the original REMUS AUV and built an AUV operations group at WHOI which possesses specialty in conducting REMUS 6000 explorations anywhere around the world.
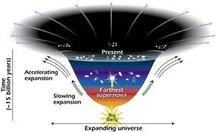 According to a study, x-ray measurements of outlying galaxy clusters validate the theory that dark energy is driving the universe to expand immeasurably.
The findings suggest that the dark energy pushes away every matter in the universe, and it will continue pushing them further—or away—until none of the galaxy except the nearest Andromeda galaxy would be observable from planet Earth.
Scientists who conducted the study, have also started to endorse the concept that the dark energy is the alleged cosmologic constant.
The head of the research, Dr. Alexey Vikhlinin of Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Cambridge, MA, says, "Putting all of this data together gives us the strongest evidence [to the claim] that [the] dark energy is the cosmological constant."
Prof. David Spergel, astrophysicist at New Jersey Princeton University who didn’t contribute on the research, also agrees.
"Even nothing--empty space--weighs something, and because we have a lot of nothing, it [made] a major [contribution] in the evolution of our universe and [has] caused space itself to accelerate," Spergel said.
Vikhlinin and his team employed the orbiting Chandra x-ray observatory of NASA to look at the superclusters of galaxy–the collapsed globs that count as the biggest-known objects in the entire universe.
The measurements of these galaxy superclusters indicate that something is decelerating their development.
"The observable universe, in terms of mass, is already shrinking," Spergel said.
 Chinese President Hu Jintao states that developing China into a nation of innovation must be undertaken as its future-oriented major strategy. Hu is also the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee’s general secretary. During the meeting with 3,000 participants, Hu states that the strategy must focus on the economic development in the areas of international science and technology. He said that China should develop its strategic plans of independent innovation and speed up the development of the State innovation mechanism.
Hu described independent innovative competence as the centre of competitiveness. He said that a nation should emphasise independent invention that will lead to the progress and benefit of the world. The president said that China must support the spirit of independent innovation then improve its mechanism for innovation. The state should also advocate innovation by integrating or learning from imported technology.
Hu said that China needs to make great and meticulous effort to promote the importance of high technology, particularly the technologies with academic property rights and auxiliary technologies, which will have a great role in advocating economic growth and restructuring growth patterns. The president said that China made discoveries in several major technologies. The manned space project served to cultivate and train a group of young people and competent space experts and professionals. Several companies, organisations and over 100,000 scientific workers are involved in the project.
 The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Hubble Space Telescope caught Ganymede playing ‘peek-a-boo’. In the crisp Hubble picture, Jupiter’s largest moon shows before it ducks behind the huge planet.
The Ganymede finishes an orbit around the huge planet in every seven days.
Composed of ice and rock, Ganymede is considered the largest moon in the whole solar system. It is even larger to the planet Mercury. Ganymede resembles a dirty snowball just like Jupiter, the biggest planet in the solar system. Jupiter is very big that just a portion of the Southern Hemisphere can be seen in the pictures.
The view of Hubble is sharp that the astronomers see features on the surface of Ganymede, most especially the white crater, Tros, ray system, and the bright streaks of object blasted from the crater. The Tros and the ray system are about Arizona’s width.
The picture also demonstrates the Great Red Spot of Jupiter, the big eye-shaped feature in the upper left. The storm is the size of two Earths, the Great Red Spot is raging for over 300 years. The sharp view of Hubble of the large planet reveals the cloud’s texture in the Jovian atmosphere and several other vortices and storms.
The astronomers utilise the pictures in studying the upper atmosphere of Jupiter. As Ganymede moves across behind the large planet, it reflects the sunlight that passes in the Jupiter’s atmosphere.
 Mars’ climate cycles, which lasted for millions of years, have left rhythmic pattern records on thick sedimentary rock layers. The 3-dimensional detail of the records was revealed by one of the telescopic cameras by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter of NASA. With the use of High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera, researchers reported that is was the first ever measurement of a periodic signal on the rock layers on Mars.
Inside the four craters of the Arabia Terra region in Mars, the rock layers, with similar thickness, were repeated from dozens to hundreds of times. In one crater, the Becquerel is a bundle of 10-layer patterns repeated about 10 times. It is said to correspond in the pattern of changes of Mars’ rotation axis.
Kevin Lewis, author of a report published in the Journal Science, stated, “Each layer has weathered into a stair step in the topography where material that's more resistant to erosion lies on top of material that's less resistant to erosion”.
Some of the periodic changes appear to have affected the resistance of the rock-forming sediments, thus, some of them are formed less than three-feet thick.
The principal investigator of the images, Alfred McEwen from the University of Arizona in Tucson, said, “It's easy to be fooled without knowing the topography and measuring the layers in three dimensions”. He added, “With the stereo information, it is clear there's a repeating pattern to these layers”.
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed